Economic Life
Agriculture and Extraction
Mexico is one of the top producers of crops in the world.
Crop production accounts for 50% of Mexico's agricultural output, and is the most important agricultural activity in Mexico. Fruits and vegetables are the most economically significant agricultural products exported by Mexico, due to the climate and land encompassed by the region.
Livestock on the other hand accounts for about 30% of Mexico's agricultural output. The livestock most predominantly produces eggs, milk, poultry, and beef. The northern part of Mexico has been considered the most important ranching area in the country since the Mexican War of Independence.
Mexico is a major oil producer and exporter. Mexico is the 6th largest crude producer of oil, and the 10th largest exporter. Declining reserves and production along with a gradual increase in consumption could turn Mexico into a net oil importer within the next decade.
Manufacturing and Service Industries
There are a variety of major manufacturing industries in Mexico, these industries include:
 Aerospace
AerospaceOne of the three largest industries manufacturing in Mexico today. This industry has proven to be extremely lucrative and will create more than 35,000 jobs over the next five years. Mexico has become the location of choice for aerospace companies seeking a low-cost manufacturing footprint in North America.
Automotive
Automotive is rapidly growing in Mexico. Large auto companies, such as Nissan and Mazda, are fueling this growth by establishing manufacturing plants throughout the country. Mexico could be considered one of the most diverse automotive markets in the world.
Clean Energy
Solar and wind turbine industries are two of the many growing industries manufacturing in Mexico. The solar industry in Mexico is viewed by analysts as possibly the best location in North America due to the area of land in hot sunny regions, its extensively diverse labor pool, and its proximity to the United States. If less than one percent of Mexico's land was developed for the purpose of solar energy, it could provide enough power to sustain the entire nation.
Electronic
With a majority of Mexico's electronic production located near the United States border, the electronics industry was one of the first to begin manufacturing in Mexico. Tax incentives, training programs and special agreements has been the driving factor behind Mexico manufacturing. With programs to help the growth of manufacturing, a well-trained, young workforce is available to companies who want to manufacture in Mexico.
Industrial
Similar to the electronic manufacturing, industrial manufacturing plants are mainly located near the U.S. boarder for easy exportation. This includes assembling components and manufacturing raw materials.
Textiles
Textile manufacturing in Mexico accounted for many maquiladora operations along the border until the late 1990’s and early 2000’s. Specialty textiles for the filter, automotive and medical device industries continue to expand in Mexico. More textile manufacturers are once again exploring Mexico as a viable option due to hyperinflation in China. Now that the minimum wage in Mexico is competitive with China, clothing manufacturers are “re-shoring” their operations back to Mexico.
The manufacturing industries of Mexico are all quite competitive and rapidly growing throughout the nation. Among the industries listed Electronics, Medical Devices, and Metal Mechanics are also large manufacturing industries in Mexico.
Economy and Development
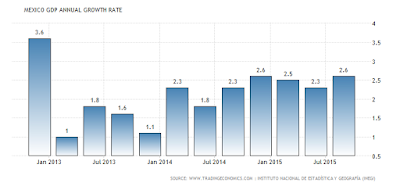
The expansion of economic activity will rely on growth of private consumption and investment, with an increase in manufacturing exports following the significant real exchange rate adjustment and robust growth in the U.S. eventually providing additional support.
A complicated global environment will continue to weigh on Mexico’s economic growth prospects. The Mexican authorities have already signaled their commitment to appropriate fiscal and monetary policy tightening aimed at maintaining macroeconomic stability.
Main Challenges
Today, Mexican manufacturers compete head-to-head with China's, often in the same product lines, and despite Mexico's strategic geographic advantage close to US markets, Chinese labor costs and production volumes are making it difficult for Mexico to preserve it share if US and global markets.
Mexico has nine years left of proven oil reserves, and average daily production is falling steadily. This trend casts a worrisome shadow on the country's fiscal future, as oil revenues have traditionally accounted for some 40 percent of the government's budget.
Ninety percent of Mexico's exports and 70 percent of its imports go to and come from the United States, while some 65 percent of Mexico's foreign direct investment comes from US investors. If the American economy goes south, Mexico will not stand an independent chance.
Mexico has nine years left of proven oil reserves, and average daily production is falling steadily. This trend casts a worrisome shadow on the country's fiscal future, as oil revenues have traditionally accounted for some 40 percent of the government's budget.
Ninety percent of Mexico's exports and 70 percent of its imports go to and come from the United States, while some 65 percent of Mexico's foreign direct investment comes from US investors. If the American economy goes south, Mexico will not stand an independent chance.
Internet Sources:
http://www.nationsencyclopedia.com/economies/Americas/Mexico-AGRICULTURE.html
http://www.resourcegovernance.org/countries/latin-america/mexico/extractive-industries
http://www.napsintl.com/manufacturing-in-mexico/industries-in-mexico/
http://www.worldbank.org/en/country/mexico/overview
http://www.napsintl.com/manufacturing-in-mexico/industries-in-mexico/
http://www.worldbank.org/en/country/mexico/overview